Thank Dave. M. Gray for the help to modify the makefile
1. NPSOL 5.0 needs to be ordered from http://www.sbsi-sol-optimize.com/asp/sol_product_npsol.htm
After you get npUnix.tar.gz, you can extract it.
You got a directory contains GNUmakefile....
In order to compile and install NPSOL, you need install F2C first, and set the environment variable F2C , for example, in my computer, F2C is installed in /usr/
In command line
export F2C=/usr/
gmake
gmake clean
Therefore, NPSOL will be installed, a new directory will be created (npsol/Linux-i686/optimized/lib) the created directory is dependent on your own system.
2. Download npsol (it is an AMPL interface to NPSOL 5.0) from
http://netlib.bell-labs.com/netlib/ampl, it is a file called netlibfiles.tar
extract netlibfiles.tar , you get solvers/
in solvers/ directory, you may have many .gz files
gunzip *.gz
make -f makefile.u (it depends on your system)
Then amplsolver.a is created in this directory
3. Now go to solvers/npsol
copy all NPSOL library files (/npsol/Linux-i686/optimized/lib) to this directory.
make -f makefile.u
Attention, you may read makefile.u carefully, make some necessary changes according to your system.
cp makefile.u makefile
in makefile
"n = npsol.o version.o $S/amplsolver.a libnpsol_f77.a libblas_f77.a libnlssol_f77.a liblssol_f77.a
npsol: $n
$(CC) -o npsol $n -lf2c -lm -ldl" for my system,Linux localhost 2.6.24-21-generic #1 SMP Tue Oct 21 23:43:45 UTC 2008 i686 GNU/Linux
type make -f makefile
the executable npsol will be created in this directory.
4. Set PATH variables to make the system find this executable
in command line, gedit .bashrc, add npsol path, source .bashrc
5. in AMPL program, just use option solver npsol.
It should work.
Thursday, December 4, 2008
Thursday, November 20, 2008
File output and input in Matlab and C
Save matlab workspace variables to a text file
save('filename','variable_name','-ASCII');
Scan this file into a C program
int k1;
FILE *filename;
filename = fopen("filename","r");
for (k1 = 0; k1 < size; k1++)
fscanf(filename, "%f ", &var[k1]);
fclose(filename);
save('filename','variable_name','-ASCII');
Scan this file into a C program
int k1;
FILE *filename;
filename = fopen("filename","r");
for (k1 = 0; k1 < size; k1++)
fscanf(filename, "%f ", &var[k1]);
fclose(filename);
Saturday, November 15, 2008
Weird problems in C debugging
./opt1.sub.h: In function ‘tcf’:
./opt1.sub.h:234: error: stray ‘\357’ in program
./opt1.sub.h:234: error: stray ‘\274’ in program
./opt1.sub.h:234: error: stray ‘\213’ in program
./opt1.sub.h:234: error: expected ‘)’ before ‘zp’
I searched the web, the problem is"
It means you have some goofy characters on that line. They are probably invisible. Try deleting the line entirely and retyping it."----from cprogramming.com
./opt1.sub.h:234: error: stray ‘\357’ in program
./opt1.sub.h:234: error: stray ‘\274’ in program
./opt1.sub.h:234: error: stray ‘\213’ in program
./opt1.sub.h:234: error: expected ‘)’ before ‘zp’
I searched the web, the problem is"
It means you have some goofy characters on that line. They are probably invisible. Try deleting the line entirely and retyping it."----from cprogramming.com
Monday, November 10, 2008
Ubuntu Desktop Recover
Sometimes, when you install new programs on Ubuntu, you may fail to log into the graphic interface again.
In that case, you may try to reinstall ubuntu-destkop by
"sudo apt-get install ubuntu-desktop".
Generally, after rebooting, you will be able to access to the desktop again.
If "xorg.conf" under the /etc/ directory may be corrupted. You can use the backup from that directory by
"cp xorg.conf.backup xorg.conf"
In that case, you may try to reinstall ubuntu-destkop by
"sudo apt-get install ubuntu-desktop".
Generally, after rebooting, you will be able to access to the desktop again.
If "xorg.conf" under the /etc/ directory may be corrupted. You can use the backup from that directory by
"cp xorg.conf.backup xorg.conf"
Thursday, October 30, 2008
Set $PATH on Ubuntu
Sometimes the program needs to find the right location to execute.
For example, AMPL is hooked with IPOPT, AMPL needs to know where to find IPOPT. To set PATH variable on Ubuntu (or any other Linux) system is easy for them to work together.
Three steps:
1, open a terminal
2, sudo gedit .bashrc
3, add
PATH=${PATH}:your_directory/bin;
export PATH
4, source .bashrc
5, echo $PATH
That should make AMPL to find IPOPT executable.
¨export CC=gcc¨, when you encountered a configuraion or make problem, you may need to add this command before you configure or make your program.
For example, AMPL is hooked with IPOPT, AMPL needs to know where to find IPOPT. To set PATH variable on Ubuntu (or any other Linux) system is easy for them to work together.
Three steps:
1, open a terminal
2, sudo gedit .bashrc
3, add
PATH=${PATH}:your_directory/bin;
export PATH
4, source .bashrc
5, echo $PATH
That should make AMPL to find IPOPT executable.
¨export CC=gcc¨, when you encountered a configuraion or make problem, you may need to add this command before you configure or make your program.
Sunday, October 26, 2008
Batch convert jpg to eps on Ubuntu
Tried to find the way to convert jpg to eps in a batch mode.
It is difficult to find it online.
Thus, I record my method here.
In command line:
1. install imagemagick (sudo apt-get install imagemagick)
2. for i in *.jpg; do convert $i $i.eps; done
If there are "i" in the pictures names, it may cause the problem, in order to avoid this problem, you may replace "i" with "z"
It will keep the file name unchanged.
It is difficult to find it online.
Thus, I record my method here.
In command line:
1. install imagemagick (sudo apt-get install imagemagick)
2. for i in *.jpg; do convert $i $i.eps; done
If there are "i" in the pictures names, it may cause the problem, in order to avoid this problem, you may replace "i" with "z"
It will keep the file name unchanged.
Tuesday, July 29, 2008
Network sharing with Ubuntu
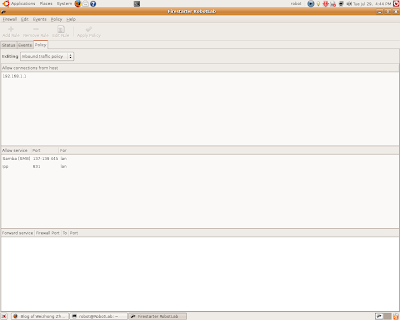 The following procedures to share your internet connection and printer in your local network with Ubuntu as the server
The following procedures to share your internet connection and printer in your local network with Ubuntu as the server1. Hardware, two network cards for the server, assuming one is eth0 for connecting the outside(IP address is assigned by your ISP, Net mask and DNS should also be provided), eth1 (IP address can be assigned as 192.168.1.1) for connecting the local network, one hub to connect the local computers.
2. Make sure your hardwares are connected well, first the server can be connected to the internet, then use ping command to test whether the clients are connected to the server or not.
.
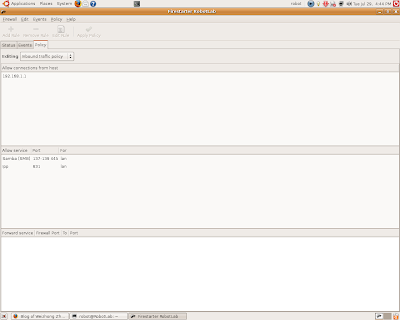
3. Use firestarter to configure the server to make the dhcp, printer service(different in windows and (Port 631) unix) ports open to the local network.
4. On the server, start dhcpd daemon, start cupsd daemon.
5. Configure the client computers as dhcp to use the internet, use CUPS (For Unix only, for windows, use the control panel to add the printer by searching the local network).
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
